The UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) has announced the publication of the Global Education Digest 2008: Comparing Education Statistics Across the World. This annual publication contains detailed statistical tables with the latest UIS data on pre-primary, primary, secondary and tertiary education, education finance and literacy.
The UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) has announced the publication of the Global Education Digest 2008: Comparing Education Statistics Across the World. This annual publication contains detailed statistical tables with the latest UIS data on pre-primary, primary, secondary and tertiary education, education finance and literacy.The introductory chapters in the this year's edition of the Digest discuss the data collection process at UIS, the International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED) and differences between national and international education data, the use of historical time series to track educational trends, and programs of cooperation between UIS and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the Statistical Office of the European Communities (Eurostat).
The Global Education Digest 2008 contains several tables that were not available in the 2007 edition. New tables with time series data provide statistics for more than 200 countries and territories from 1970, 1980, 1990, 2000 and 2005 for the following indicators: primary and secondary school age; population of secondary school age (the population of primary school age is available at the UIS Data Centre, see below); enrollment in primary, secondary and post-secondary education; total enrollment from primary to tertiary education; primary and secondary school gross enrollment ratio (GER); primary school gross intake ratio; gross intake ratio to the last grade of primary school (a proxy indicator for the primary completion rate); repetition rate in primary and secondary school; school life expectancy (primary to secondary and primary to tertiary); pupil/teacher ratio in primary and secondary school; and public expenditure on education.
A further addition in the new publication is a set of tables with data for 62 UOE and WEI countries. UOE refers to a joint data collection program by UIS, OECD and Eurostat in high- and middle-income countries. WEI stands for World Education Indicators, a UIS program for middle-income countries. The participating countries are listed on pages 30 and 31 of the Global Education Digest 2008.
The data from the tables in the Global Education Digest can be downloaded from the UIS Data Centre (click on "Predefined Tables" and then "Education"). The time series data for the years 1970 to 2005 are available in Excel format in Tables 21 to 23. The population of primary school age between 1970 and 2005 is not shown in the printed report but included in Table 21. In addition, the Data Centre offers annual data for the years 1999 to 2008, while the Digest only shows data for one or two years, depending on the indicator.
References
- UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS). 2008. Global education digest 2008: Comparing education statistics across the world. Montreal: UIS. (Download PDF, 7.3 MB)
- UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS). 2007. Global education digest 2007: Comparing education statistics across the world. Montreal: UIS. (Download PDF, 3.7 MB)
- UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
- Announcement of the Global Education Digest 2008 by UIS
- UIS Data Centre
- Global Education Digest 2009
- Global Education Digest 2007
- EFA Global Monitoring Report 2009
- UN Millennium Development Goals Report 2008
- Primary completion rate 2002/03
Permanent URL: http://huebler.blogspot.com/2008/12/ged.html

 UNESCO released the 2009 edition of the
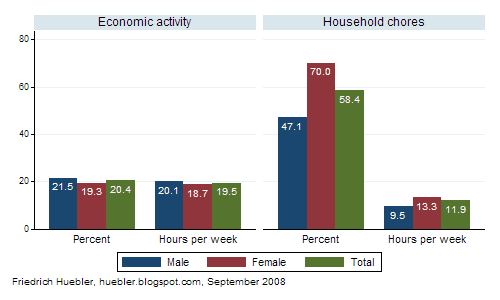
UNESCO released the 2009 edition of the  The Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys (MICS) are household surveys carried out in developing countries with the support of UNICEF to collect data on the situation of children and women. The most recent round of MICS surveys was conducted between 2005 and 2007 in more than 40 countries. MICS data and documentation are available at the
The Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys (MICS) are household surveys carried out in developing countries with the support of UNICEF to collect data on the situation of children and women. The most recent round of MICS surveys was conducted between 2005 and 2007 in more than 40 countries. MICS data and documentation are available at the 


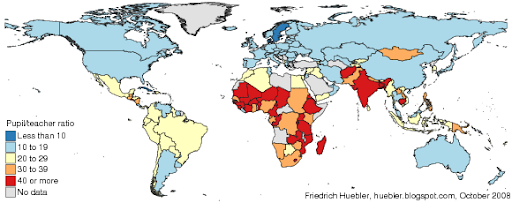
 In August 2008, the United Nations published the latest edition of its annual report on progress toward the
In August 2008, the United Nations published the latest edition of its annual report on progress toward the 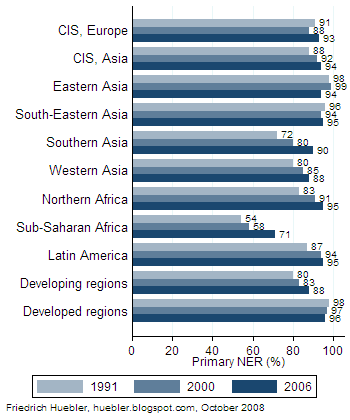
 A new
A new